 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Tab stopsThe list at the top right hand side of the broadly demonstrates a list of tabstops. The list is in order, so the stop at the top of the list, is the leftmost one. Each successive tabstop entry in the list is found, in the document, to the right of the one that preceeds it in the list. There are different types of tabstop, each with a different function. Although it is possible to individually specify the position of each tabstop, it is more likely that more capable tabstop types will be used, and then there will be less tabstops in the list, than are present in the actual document. The screenshot below shows the tabstops list of the line types dialog, used for assembly language text files; 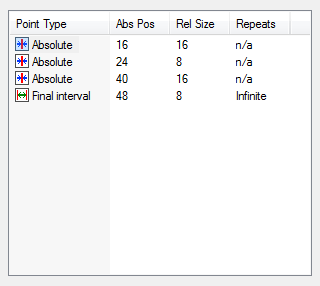 The following tabstop types are available;
In addition to the above types, a subcategory of the interval tabstop is common to all line types. The final interval tabstop, is always the last tabstop in any line type. It will simply repeat to infinity, and ensures that there is always a "next tabstop" on any given document line, irrespective of how long the line might be. In general, certain combinations of tabstops are not practical to implement. Typically an interval tabstop cannot follow another interval tabstop, because there is no way to explicitly define the number of tabstop repeats. If it is genuinely necassary to change the interval of repeating tabstops, then an absolute tabstop must be calculated as the last of the previous group of repeating tabstops, and the first of the next. In the same way, a relative tabstop cannot follow an interval tabstop, since it is not possible to determine which of the repeat intervals is the last from which the relative tabstop is offset. There are two methods available for adding tabstops. The first involves the use of the small buttons above the list on the right of the dialog. The second method is available through a right click context menu, available in the list window. The latter scheme also provides the capability to modify the tabstops through the "properties" menu item. Tabstop entried can be removed with the delete command on the context menu. Both of the properties and delete functions act on the currently selected list item. In respect of additions the general aim is to add a new tabstop prior to the currently selected item. In some cases, there will be insufficient room for a repeating or relative tabstop. In these cases addition is prevented with a notification dialog. Also, one tabstop may eclipse another. In this circumstance one or other will be removed. If, in the case of an absolute tabstop, the actual position of the tabstop is not correct in relation to those that surround it, the list will be automatically reordered. |
Copyright © Solid Fluid 2007-2025 |
Last modified: SolFlu Wed, 07 Oct 2009 17:52:40 GMT |